1. 前言
单例模式是一种创建型设计模式, 让你能够保证一个类只有一个实例, 并提供一个访问该实例的全局节点,有很多种实现方式
- 饿汉式,也就是类初始化时直接创建对象
- 懒汉式,在调用函数时创建对象
- 静态内部类,在外部类初始化时静态内部类并不会被初始化,延迟初始化类获取单例实例
- 枚举
他们都有一个特性,构造器私有化
2.实现
2.1 饿汉式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class Singleton {
private Singleton() {
}
private static final Singleton singleton = new Singleton();
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return singleton;
}
}
|
这种方式最直接,在类装载时就会实例化对象,不会存在线程安全问题,可能不符合某些需求
2.2 懒汉式
2.2.1 线程不安全
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class Singleton {
private Singleton() {
}
private static Singleton singleton = null;
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Singleton();
}
return singleton;
}
}
|
2.2.2 线程安全
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class Singleton {
private Singleton() {
}
private static Singleton singleton = null;
public static synchronized Singleton getInstance() {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Singleton();
}
return singleton;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class Singleton {
private Singleton() {
}
private static Singleton singleton = null;
public static Singleton getInstance() {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Singleton();
}
}
return singleton;
}
}
|
效率低,所以引出 DCL
2.3 DCL(Dobule Check Locking)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class Singleton {
private Singleton() {
}
private static volatile Singleton singleton = null;
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
}
|
2.4 静态内部类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class Singleton {
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
return SingletonHolder.instance;
}
static class SingletonHolder {
private static final Singleton instance = new Singleton();
}
}
|
利用静态内部类延迟初始化机制,实现懒加载,并且不会出现线程安全问题
2.5 反射破坏
上面方式尽管解决了一些问题,但还是免不了被反射破坏,反射是 Java 一个强大的特性,下面用反射破坏一下单例模式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| Singleton instance = Singleton.getInstance();
System.out.println(instance);
Class<? extends Singleton> aClass = instance.getClass();
Constructor<? extends Singleton> constructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor();
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Singleton singleton = constructor.newInstance();
|
2.6 枚举
枚举是一个特殊的类,一般表示常量,它也可以实现单例,并且是一个很好的选择
在上面讲过了几种单例实现方式,都会被反射破坏,但是枚举不会
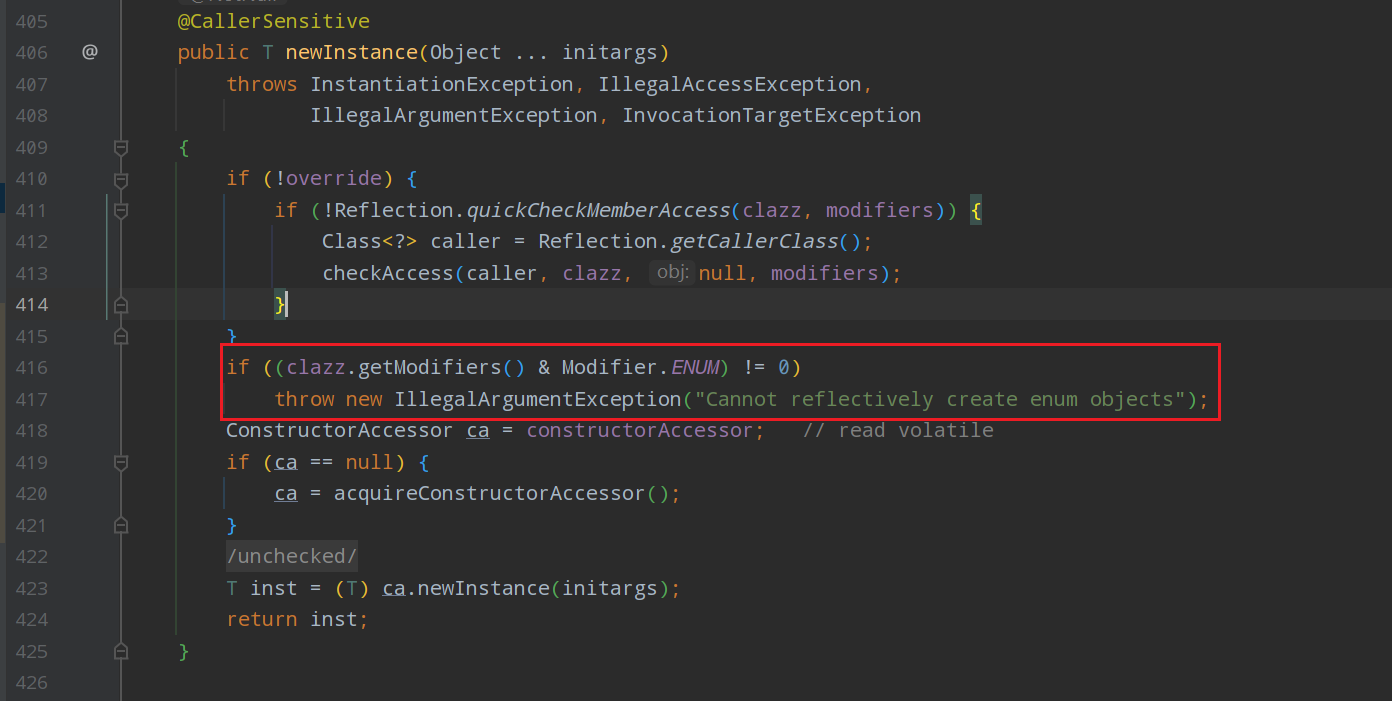
无法通过反射创建枚举对象,我们可以用这个特性去实现单例模式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public enum Singleton {
INSTANCE;
Singleton() {
}
}
|
单例模式的使用场景还是很多的 ,最常见的就是强大的 Spring框架,然后计数,缓存等等
